Does Metoprolol Cause Hair Loss? Understanding the Risks
Introduction to Metoprolol and Hair Loss
Metoprolol is a commonly prescribed beta-blocker often used to treat high blood pressure, heart conditions, and anxiety. While it is effective in managing these conditions, patients frequently express concerns regarding potential side effects, particularly hair loss. The question remains: does metoprolol cause hair loss? Understanding the risks associated with this medication is crucial for patients considering or currently using metoprolol. In this article, we will explore the connection between metoprolol and hair loss, the mechanism behind any potential effects, and alternative treatment options for managing side effects.

Understanding Metoprolol and Its Mechanism of Action
1. What is Metoprolol?
- Drug Classification: Does metoprolol cause hair loss? Metoprolol is classified as a selective beta-1 blocker. Its primary function is to block the effects of adrenaline on the heart. This action helps decrease heart rate and lower blood pressure, which can reduce the risk of heart-related issues.
- Medical Uses: This medication is commonly prescribed for various conditions, including hypertension (high blood pressure), angina (chest pain), and heart failure. Additionally, it is utilized to prevent migraines and manage anxiety.
- Administration Forms: Metoprolol is available in different forms, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, as well as an injectable form used in emergency situations.
2. How Does Metoprolol Work?
Beta-1 Adrenoceptor Blocking
1. Understanding Beta-1 Adrenergic Receptors
- Receptor Location: Beta-1 adrenergic receptors are primarily located in the heart. They are a type of G-protein-coupled receptor that responds to catecholamines such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are hormones involved in the body’s fight-or-flight response.
- Role in Heart Function: These receptors play a critical role in regulating heart rate and the force of heart contractions. When stimulated, they increase heart rate (chronotropy) and the amount of blood pumped per contraction (inotropy).
2. Mechanism of Action of Metoprolol
- Selective Targeting: Metoprolol is classified as a selective beta-1 blocker, meaning it primarily affects beta-1 adrenergic receptors without significantly influencing beta-2 receptors, which are found in the lungs and vascular smooth muscle. This selectivity helps in minimizing respiratory side effects.
- Efficiency in Reducing Heart Rate: By inhibiting the activity of beta-1 receptors, metoprolol effectively reduces the heart rate. A lower heart rate means the heart pumps less frequently, which is beneficial for individuals with conditions like hypertension or heart failure.
- Impact on Contractility: In addition to lowering heart rate, metoprolol decreases the contractility of the heart muscle. This means the heart muscle exerts less force during contractions, thereby reducing the overall workload on the heart.
3. Effects on Blood Pressure
- Lowering Blood Pressure: The combination of reduced heart rate and contractility leads to a decrease in cardiac output, which ultimately results in lower blood pressure. This effect is particularly important for patients with hypertension, as it helps manage blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Long-term Benefits: Consistent use of metoprolol can lead to long-term cardiovascular benefits. By lowering blood pressure and controlling heart rate, it reduces the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related issues.
Secondary Effects
1. Body’s Response to Stress
- Adrenaline and Stress Response: When the body encounters stressful situations, it releases adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine). These hormones prepare the body for immediate action, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and energy availability.
- Potential Harmful Effects: While these hormone releases are vital for survival in acute situations, they can be detrimental in chronic stress scenarios. Prolonged exposure to high adrenaline levels can lead to excessive strain on the heart and increased risk of cardiovascular events.
2. Mitigating Harmful Effects of Adrenaline
- Role of Metoprolol: By blocking beta-1 receptors, metoprolol effectively mitigates the effects of stress-induced adrenaline secretion. This action helps prevent over-activation of the cardiovascular system.
- Reduced Heart Workload: The inhibition of beta-1 receptors leads to a decrease in heart workload during stressful situations. This response helps maintain a more stable heart rhythm and prevents potential complications associated with high-stress levels.
3. Overall Cardiovascular Protection
- Long-Term Cardiovascular Health: Metoprolol’s ability to mitigate the harmful effects of stress hormones contributes significantly to overall cardiovascular health. It helps protect the heart from damage that can result from chronic stress, such as left ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure.
- Improved Quality of Life: By effectively managing heart rate and blood pressure, metoprolol can enhance quality of life for patients with heart problems, allowing them to lead more active and less stressful lives.
Potential Side Effects of Metoprolol
1. Common Side Effects
- General Information: Like any medication, metoprolol can cause a range of side effects. Some of the most common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, depression, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Less Frequent But Significant: Although rarer, side effects such as shortness of breath, swelling in the extremities, and decreased libido may occur. A thorough discussion with a healthcare provider is essential for identifying these symptoms early.
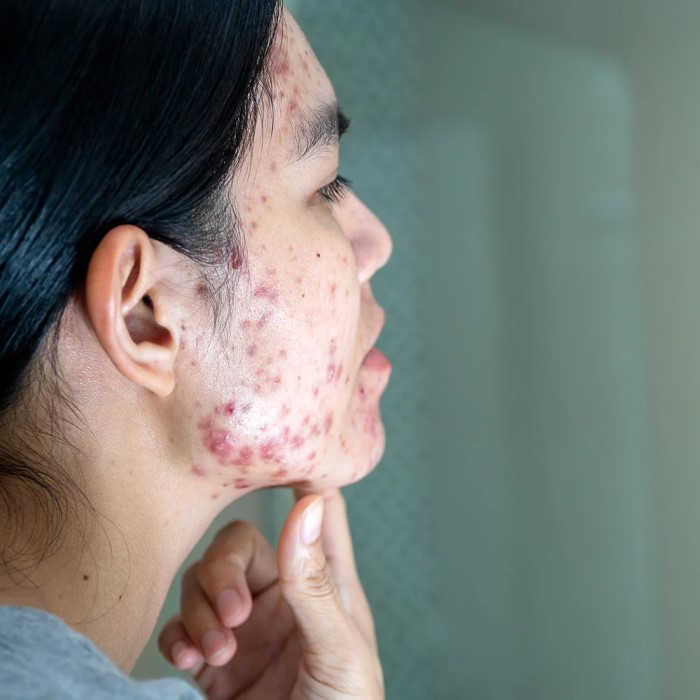
2. Hair Loss: A Potential Risk
- Connection with Hair Loss: There are anecdotal reports of hair loss associated with metoprolol use. However, it is essential to clarify that the evidence linking metoprolol directly to hair loss is still inconclusive.
- Mechanisms Behind Hair Thinning: Hair loss may be attributed to various factors, including hormonal changes, stress, or overall health conditions, rather than solely the medication.
- Research Insights: Some studies suggest that beta-blockers, like metoprolol, could potentially affect hair growth by altering blood flow or hormonal balance. However, definitive proof is still lacking.
Investigating the Link Between Metoprolol and Hair Loss
1. Patient Experiences and Studies
- Anecdotal Evidence: Many patients report experiencing hair thinning or loss after starting metoprolol. These instances lead to concerns about the medication’s long-term effects, especially among those already prone to hair loss.
- Clinical Studies: Current clinical research has not definitively established that metoprolol causes hair loss. Continued studies are needed to understand better the correlation between beta-blockers and hair thinning.
- Hair Growth Cycles: Hair goes through cycles of growth, rest, and shedding. Factors that may disrupt these cycles can contribute to hair loss, including medications, stress, and underlying health issues.
2. Is Hair Loss from Metoprolol Reversible?
- Reversibility Factors: If hair loss occurs as a result of taking metoprolol, many patients inquire whether it is reversible. In most cases, hair regrowth is possible, but it may depend on individual circumstances.
- Transitioning Medications: If a patient stops using metoprolol or transitions to another medication, any hair loss may be resolved as the body readjusts. Consulting with a healthcare provider about this possibility is crucial for determining the best course of action.
Managing Hair Loss While Taking Metoprolol
1. Consultation with Healthcare Providers
- Assessment of Health Conditions: If hair loss occurs after starting metoprolol, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to assess whether the medication is the underlying cause or if other factors are at play.
- Exploration of Alternatives: Physicians may consider adjusting dosages or exploring alternative medications that may achieve similar therapeutic results without the potential side effects of hair loss.
2. Treatment Options for Hair Loss
Non-Invasive Treatments
1. Topical Minoxidil
- Overview of Minoxidil: Topical minoxidil is an FDA-approved treatment commonly used for hair regrowth. It is applied directly to the scalp and has been shown to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
- Mechanism of Action: Minoxidil works by increasing blood flow to hair follicles, which helps deliver essential nutrients and oxygen. This improved circulation can revitalize dormant hair follicles and encourage them to enter the growth phase, leading to thicker hair over time.
- Application Regimen: Typically, minoxidil is applied twice daily for optimal results. Consistency is key; users should follow instructions carefully to maximize effectiveness. Users may start noticing results after about four to six months, although individual experiences may vary.
2. Other Hair Growth Products
- Alternative Treatments: Beyond minoxidil, several other topical treatments and products aim to promote hair growth. Options may include scalp serums, essential oils (such as rosemary or peppermint oil), and herbal formulations.
- Nutritional Support: Some hair growth products contain vitamins and nutrients like biotin, vitamin E, and saw palmetto, which are believed to support hair health. These ingredients can sometimes be found in shampoos, conditioners, and supplements.
- Consultation with Professionals: Before starting any new treatment, it’s wise for patients to consult with healthcare providers or dermatologists. Professionals can recommend suitable products based on individual needs and hair loss causes.
Lifestyle Considerations
1. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious, balanced diet plays a crucial role in hair health. Consuming adequate amounts of protein, vitamins, and minerals is essential for maintaining healthy hair. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and iron can be particularly beneficial.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is another important factor. Drinking enough water supports overall health and helps keep the scalp and hair follicles nourished, potentially promoting better hair growth.
2. Stress Management Techniques
- Impact of Stress: High levels of stress can significantly contribute to hair loss. Stress-related conditions, such as telogen effluvium, can lead to increased shedding. Therefore, managing stress is vital for maintaining healthy hair.
- Stress Reduction Practices: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can alleviate stress and promote relaxation. Regular physical activity can also help reduce stress hormones and improve overall well-being.
- Seeking Support: Engaging in hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or consulting professionals for counseling can provide additional support in managing stress effectively.
3. Scalp Care
- Importance of Scalp Health: A healthy scalp is crucial for hair growth. Excess buildup of products, dirt, and excess oils can inhibit hair follicles, leading to issues such as clogged pores and inflammation.
- Regular Cleansing: Incorporating a gentle cleansing routine can help maintain scalp health. Choose sulfate-free shampoos to avoid stripping natural oils and promoting irritation.
- Exfoliation and Massage: Regular scalp exfoliation can promote hair health and clear buildup. Additionally, gentle scalp massages improve blood circulation, which may encourage hair growth by ensuring that hair follicles receive adequate nutrients.
FAQs About Metoprolol and Hair Loss
1. Is hair loss from metoprolol reversible?
- Yes, hair loss that potentially results from metoprolol can be reversible in many cases. Once the medication is adjusted or discontinued, hair regrowth may occur.
2. Which beta blocker causes the most hair loss?
- While each individual responds differently to medications, some reports suggest that non-selective beta blockers may have a higher association with hair loss compared to selective blockers like metoprolol.
3. How to stop hair loss from beta blockers?
- If hair loss occurs, consult with a healthcare provider to explore potential alternatives or treatment options. Certain topical agents and lifestyle changes may also support hair regrowth.
4. What are the most common side effects of metoprolol?
- Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, depression, and gastrointestinal issues. More serious concerns include respiratory issues and swelling in the extremities; if experienced, patients should seek immediate medical advice.
Conclusion: Does Metoprolol Cause Hair Loss?
In summary, while many patients wonder does metoprolol cause hair loss, the connection remains largely unclear. Anecdotal evidence exists, but research has yet to establish a direct causal relationship. Understanding your treatment options is critical to managing any side effects while taking metoprolol.
If you’re experiencing hair loss, consult with your healthcare provider to investigate potential causes and explore suitable solutions. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare team about your concerns is vital to finding the best approach for your specific situation and ensuring overall health and well-being.