Does Lupus Cause Hair Loss? Myths and Facts You Should Know
Introduction: Understanding Lupus and Its Effects
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disorder that can impact various systems in the body, leading to a wide array of symptoms. One common question arises: does lupus cause hair loss? While many people with lupus experience changes in their hair, the connection between lupus and hair loss is often misunderstood. This article will clear up common myths and facts surrounding this topic, offering insight into how lupus affects hair health and what can be done about it.
What is Lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes the immune system to attack healthy tissues. The exact cause of lupus is still unknown, but genetic and environmental factors play a role.
This condition can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, and other organs. It is more common in women than men and can develop at any age.
There are several types of lupus:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): The most common and severe type. It affects multiple organs.
- Cutaneous Lupus: Primarily affects the skin, causing rashes and lesions.
- Drug-Induced Lupus: Triggered by certain medications, with symptoms similar to SLE. It usually subsides once the medication is stopped.
- Neonatal Lupus: A rare form affecting newborns of mothers with lupus.
Lupus is often challenging to diagnose as its symptoms mimic other conditions. Early detection and treatment are vital to managing lupus effectively and preventing further damage.
Common Symptoms of Lupus
Does lupus cause hair loss? Lupus brings about diverse symptoms, which can differ based on the type and severity of the disease. These symptoms can be temporary, long-lasting, or may flare and subside over time. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness is one of the most common symptoms of lupus.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Many patients experience pain and inflammation in their joints.
- Skin Rashes: Lupus can cause rashes, particularly on the face, known as a “butterfly rash.”
- Fever: Low-grade fever is frequently seen in lupus patients during flare-ups.
- Hair Loss: Thinning or hair loss may occur, either gradually or suddenly.
- Sensitivity to Sunlight: Many individuals become highly photosensitive, leading to sunburns or rashes.
- Chest Pain: Pain or discomfort can occur due to inflammation around the heart or lungs.
- Swollen Glands: Enlarged lymph nodes are sometimes noticeable in lupus patients.
These symptoms often overlap with other medical conditions. This can make diagnosing lupus tricky but underscores the importance of consulting a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
How Does Lupus Affect Hair Growth?
Lupus can disrupt the normal cycle of hair growth. The autoimmune nature of lupus often causes the immune system to attack hair follicles. This leads to inflammation and damage, which can hinder hair growth or result in hair loss. In some cases, the scalp can experience redness, lesions, or sores, further affecting the hair’s health.
Several factors may influence hair growth in lupus patients. Flare-ups of the disease, certain treatments, and nutrient deficiencies are all potential contributors. Managing these factors is critical to minimizing hair loss and promoting healthy hair growth.
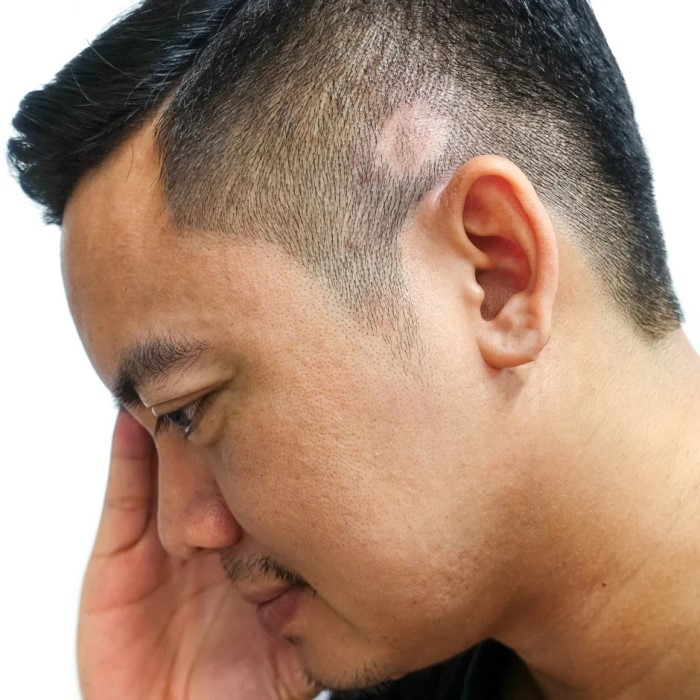
Types of Hair Loss Associated with Lupus
There are two main types of hair loss linked to lupus:
- Non-Scarring Hair Loss: This is the most common type seen in lupus patients. It typically involves thinning of hair or sudden hair shedding. The hair loss may improve during periods of remission when the disease activity is low.
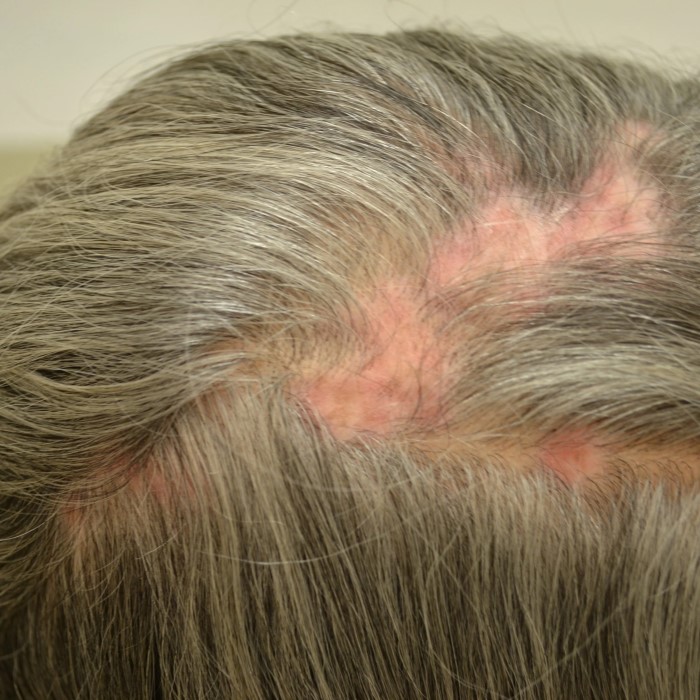
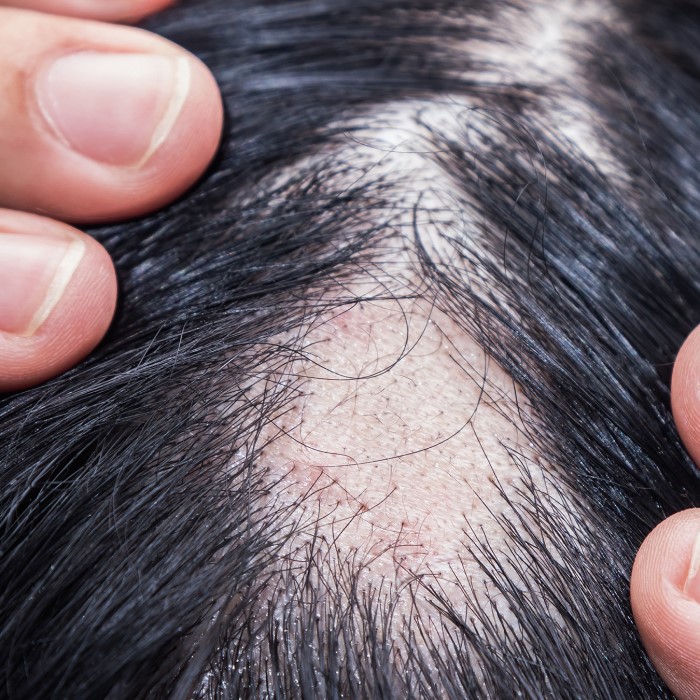
- Scarring (Cicatricial) Alopecia: This is a severe form of hair loss linked to discoid lupus erythematosus (a form of cutaneous lupus). The inflammation in the scalp can cause permanent damage to hair follicles, preventing hair regrowth. Patients may notice patches of hair loss accompanied by scaling or scarring.
Understanding the type of hair loss is important for appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help reduce damage and may prevent permanent hair loss.
Causes of Hair Loss in Lupus Patients
Lupus can lead to hair loss due to various factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for managing this condition effectively and developing a treatment plan. Two primary contributors to lupus-related hair loss are immune system dysfunction and the side effects of lupus medications.
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system plays a central role in lupus-related hair loss. Lupus, as an autoimmune disease, causes the immune system to attack healthy cells and tissues. This abnormal response often involves the hair follicles.
- Inflammation: Lupus causes inflammation in various parts of the body, including the scalp. Inflammation around hair follicles can weaken them, resulting in hair loss. In mild cases, this leads to pattern baldness or thinning of hair.
- Scalp Conditions: For those with cutaneous lupus, inflammation on the scalp creates lesions or scabs. These can further damage hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss if left untreated.
- Disease Flares: Flares or sudden worsening of lupus can increase inflammation. This worsens hair loss during an active phase of the disease.
Curbing immune overactivity through effective lupus management can help control inflammation. This approach protects hair follicles and reduces hair loss.
Side Effects of Lupus Medications
Lupus treatments can also cause hair loss as a side effect. The medications aim to control symptoms but may affect hair health.
- Immunosuppressants: These drugs suppress immune activity, reducing lupus symptoms. However, they can alter the normal hair growth cycle.
- Corticosteroids: Commonly used to manage inflammation, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to hair thinning.
- Other Medications: Drugs like methotrexate or cyclophosphamide, used for severe lupus cases, may contribute to hair shedding.
- Chemotherapy Drugs: Some treatments may damage hair follicles, similar to chemotherapy, causing temporary or permanent hair loss.
Addressing treatment-related hair loss involves close monitoring of medication doses. A doctor can recommend alternative treatments or dietary supplements when needed.
By understanding these factors, patients can work with healthcare providers to minimize hair loss. Early intervention is key to preventing long-term damage to hair growth.
Are There Different Patterns of Hair Loss in Lupus?
Yes, individuals with lupus can experience different patterns of hair loss. Hair loss due to lupus can vary widely depending on the type of lupus and the severity of symptoms. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Here are the common patterns of hair loss associated with lupus:
Diffuse Hair Thinning
One of the most common patterns is general hair thinning. This is often seen in people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The hair may become fragile, thin out evenly across the scalp, and fall out more than usual. This type of hair loss may be temporary, improving as the condition is managed.
Patchy Hair Loss
Patchy hair loss is commonly linked to scarring alopecia caused by discoid lupus. This form of cutaneous lupus creates inflamed, scarred areas on the scalp. Hair loss in these areas is usually permanent since the hair follicles are damaged.
Hair Breakage Near the Scalp
Lupus can make hair dry and brittle. This results in hair breakage near the scalp, leaving “ragged” ends. If managed early, the hair can often regrow.
Hair Loss from Medications
Certain medications used for lupus treatment can cause hair loss. This hair shedding tends to occur evenly rather than in patches. In most cases, it stops once the medication is adjusted or discontinued.
Eyebrow and Eyelash Loss
Lupus can also lead to hair loss beyond the scalp. Some individuals may lose hair from their eyebrows or eyelashes. This could occur due to systemic inflammation or skin changes near these areas.
Each pattern of hair loss associated with lupus requires a personalized approach for treatment and care. Consulting a healthcare provider early is essential for identifying the specific type of hair loss and developing a targeted plan. Understanding the different patterns helps set realistic expectations and ensures proper attention to hair and scalp health.
Diagnosis and Identifying Hair Loss Due to Lupus
Diagnosing lupus-related hair loss begins with recognizing its patterns and associated symptom. Since lupus manifests in various ways, hair loss may not initially be connected to the condition. Early evaluation is vital for effective management and treatment.
Recognizing Lupus-Related Hair Loss
Identifying hair loss patterns is crucial to diagnosis. Medical professionals observe:
- Diffuse Thinning: Systemic lupus can cause widespread, gradual thinning across the scalp.
- Patchy Loss: Discoid lupus may lead to patches of hair loss due to scarring.
- Breakage Near Scalp: Hair affected by lupus can weaken and break close to the scalp.
- Loss Beyond Scalp: In some cases, brows, lashes, or body hair may shed.
Diagnostic Tests
Doctors use specific tools and tests to confirm lupus and related hair loss:
- Scalp Biopsy: A sample from the scalp is analyzed for inflammation or damaged follicles.
- Blood Tests: ANA test detects antibodies common in lupus patients.
- Physical Examination: Visible signs like rashes or redness on the scalp help identify cutaneous lupus.
- Patient History: Information about medical and family history aids in evaluating symptoms properly.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Prompt diagnosis allows timely intervention, reducing hair loss or permanent follicle damage. If lupus is suspected, consult a healthcare provider immediately for proper evaluation. Differentiating lupus-related hair loss from other conditions ensures targeted treatment, optimizing recovery and protection of hair health.
Treatment Options for Lupus-Related Hair Loss
Lupus-related hair loss can be distressing, but effective treatments exist to help manage this condition. Treatment often requires a multi-faceted approach, combining medical interventions with lifestyle adjustments. Identifying the type of hair loss and its underlying cause is crucial for successful management. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential to develop a personalized plan.
Medications and Therapies
Medications and therapies play a significant role in treating hair loss caused by lupus:
- Corticosteroids: Often prescribed to reduce inflammation, these help prevent hair follicle damage.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: Medications like methotrexate or azathioprine curb the overactive immune system.
- Antimalarial Drugs: Hydroxychloroquine is frequently used for treating both skin and systemic lupus symptoms.
- Minoxidil: This topical treatment can stimulate hair regrowth effectively in cases of non-scarring hair loss.
- Light Therapy: Low-level laser therapy may help improve blood flow and stimulate hair follicles.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP therapy involves injecting scalp with concentrated platelets to promote hair growth.
All treatments should be used under medical guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Hair Health
Lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments and aid in improving hair health:
- Healthy Diet: Include foods rich in vitamins, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Scalp Care: Use mild shampoos and avoid harsh hair treatments or heat styling tools.
- Stress Management: Minimize stress with relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active can improve blood circulation, supporting hair and overall health.
- Protect Against Sun: Wear hats and use sun protection to prevent scalp damage from UV exposure.
- Nutritional Supplements: Consult your doctor for supplements like biotin or vitamin D to support hair growth.
Combining these approaches with medical advice can improve outcomes. Following a consistent and thoughtful care routine helps manage hair loss effectively. Regular communication with healthcare providers is key to adjusting treatment as needed over time.
Tips to Manage and Prevent Hair Loss with Lupus
Managing and preventing hair loss when you have lupus requires a proactive approach. By focusing on treatments, care routines, and lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce hair loss and improve hair health. Below are some practical tips to help:
Prioritize Scalp and Hair Care
- Use Gentle Hair Products: Choose mild, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to avoid scalp irritation.
- Avoid Harsh Treatments: Skip chemical treatments like perming, coloring, or straightening, as they can weaken hair.
- Limit Heat Styling: Minimize the use of hot tools like curling irons or blow dryers.
- Be Gentle with Hair: Use a wide-tooth comb to detangle and avoid pulling or tugging at your hair.
Protect Your Scalp
- Shield from Sun Exposure: Wear hats or use sunscreen on your scalp to prevent sun damage and rashes.
- Avoid Hair Stress: Loose hairstyles can reduce pressure on your hair roots.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep your scalp hydrated to promote healthier hair.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
- Eat Nutrient-Rich Foods: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Boost Omega-3 Intake: Foods like salmon and walnuts support scalp health and hair growth.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water daily to keep your hair hydrated and healthy.
Manage Lupus Symptoms
- Control Flare-Ups: Take prescribed medications consistently to manage lupus and reduce inflammation.
- Reduce Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness to lower stress levels.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Resting sufficiently helps your body repair and regenerate.
Monitor Medications
Some lupus medications may cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Work with Your Doctor: Regularly review your medications and dosages.
- Seek Alternatives: If a certain medication causes hair loss, ask about potential substitutes.
Consider Professional Treatments
- Use Hair Growth Products Safely: Minoxidil and other FDA-approved treatments can promote hair regrowth.
- Explore PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma can help stimulate hair growth in some cases.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy: Laser therapy can improve blood flow and support hair follicles.
Consistent care and proactive management can help reduce lupus-related hair loss. Consult your doctor for a tailored plan. Early intervention may prevent further hair loss and help regrow healthy hair.
When to See a Doctor for Hair Loss Concerns
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, especially when linked to lupus. Although some hair loss is temporary, it is important to understand when professional help is necessary. Timing your visit to a doctor can improve your quality of life and prevent further damage.
Signs to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a doctor if you notice any of the following signs:
- Sudden or Excessive Hair Loss: Losing clumps of hair or large amounts when brushing or showering.
- Persistent Scalp Irritation: Redness, itching, or painful sores on your scalp that do not heal.
- Patchy Hair Loss: Bald spots or scarring patches on your scalp.
- Hair Loss Beyond the Scalp: Loss of eyebrow, eyelash, or body hair in addition to scalp hair.
- Changes After Medication: Sudden hair loss after starting a new lupus treatment.
- Lack of Regrowth: If your hair does not grow back after a lupus flare subsides, consult a professional.
Benefits of Seeing a Doctor
- Personalized Diagnosis: Doctors can identify the type and cause of hair loss.
- Effective Treatments: Early medical intervention can improve the chances of hair regrowth.
- Scalp and Hair Health Assessment: A detailed evaluation ensures any underlying issues are addressed.
- Treatment Adjustments: Doctors may fine-tune medications to minimize hair loss side effects.
- Prevention Advice: You will get valuable tips to stop further hair loss and protect your hair.
Preparing for the Appointment
Make the most of your consultation by staying ready:
- Track Hair Loss Patterns: Note when and where your hair loss occurs.
- List Symptoms: Inform your doctor about scalp issues or other lupus-related symptoms.
- Provide Medical History: Share details about your health conditions and family history of hair loss.
- Bring Medication Details: List all medicines and supplements you are taking.
Specialist Consultations
- Dermatologist: For scalp issues, rashes, or skin-related causes of hair loss.
- Rheumatologist: To manage lupus symptoms, including hair loss caused by immune system dysfunction.
- Trichologist: For specialized hair and scalp treatments.
Hair loss due to lupus can be managed effectively with timely medical care. Seeking professional guidance ensures a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan to protect your hair and overall health.
In conclusion, the question does lupus cause hair loss? is answered affirmatively, but with a nuanced understanding. While lupus can lead to hair loss, the degree and permanence of this condition can vary greatly among individuals. Understanding the myths and the facts about lupus-related hair loss is crucial for managing expectations and treatments effectively.
Taking proactive steps through consultation, medication adjustments, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve your hair health. With the right knowledge and strategies, living with lupus and managing hair loss can become more manageable. Always prioritize self-care and consult with healthcare providers to address concerns effectively. By debunking myths and discussing the facts, individuals can navigate their lupus journey with confidence and clarity.